The display market is teeming with options, but two technologies dominate the scene: LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) and OLED (Organic Light-Emitting Diode). But how to know which one is more suitable? The key to finding the right one lies in understanding their differences.
So, this guide will equip you with all the key differences between the LCD and OLED so that you can buy the right one.
1. What Does it Mean by LCD and OLED?
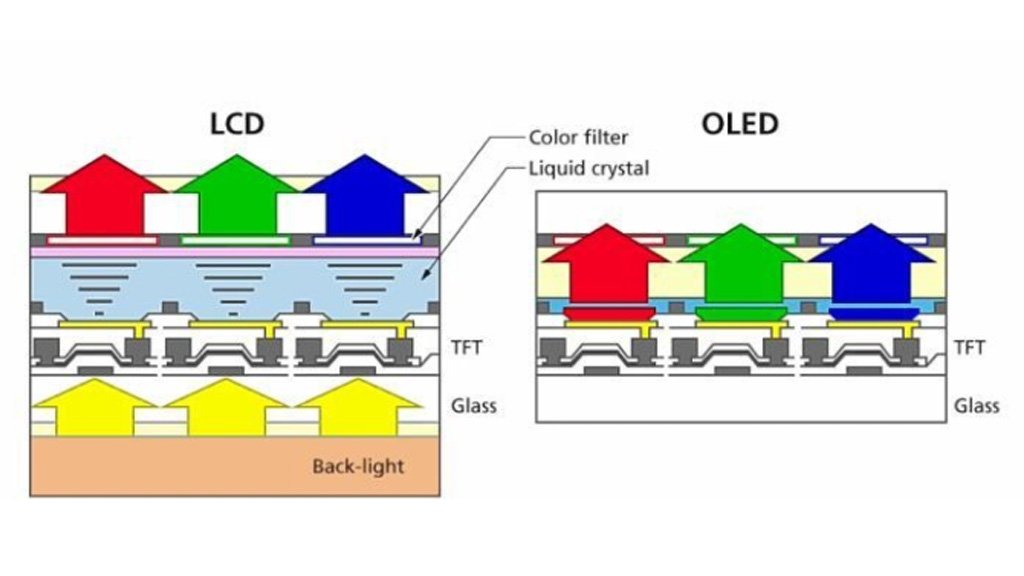
The word LCD got its name from the technology it uses which is “Liquid Crystal Display” technology. LCD functions by using liquid crystals that produce light when the electricity passes on the backend. As a result, the image appears on the display which can be viewed by the viewers.
On the other hand, OLED is a more advanced technology where light is emitted in response to the passing of current through organic molecules. It is an in-demand technology because of the higher contrast ratios, wide viewing angles, and flexibility to create even foldable and flexible displays.
2. Comparison of Core Technology
- How does LCD work?
LCD operates on liquid crystals that are sandwiched between two glass or plastic layers. When the light passes through the layer of liquid crystals, the electric current aligns them in different ways to control the amount of light that passes through.
This phenomenon creates various shades of grey, but a colour filter array is also present to produce colour images. This all is a matter of milliseconds, and it happens behind the screen whereas an array of LEDs illuminates the pixels on the screen that appear as the clear display.
- How does OLED work?
OLEDs are different from LCDs are they don’t require LEDs or any form of backlight support for illumination. Instead, the pixels in an OLED display are made up of organic compounds that are capable of emitting light upon the passing of electric current.
These organic compounds are layered carefully to produce red, green, and blue light. To have a wide spectrum of colours, the brightness of the pixels is adjusted which enables the display of the variety of colours on the screen.
3. Visual Quality and Performance
- Colour performance
In LCDs, colour accuracy varies depending on the type of LCD panel. The most widely used LCD panels are IPS (In-Plane Switching) and TN (Twisted Nematic), among which IPS offers better colour accuracy and more consistent colour reproduction.
The range of the colours that the LCD can display is measured by its ‘colour gamut.’ High-end LCDs can cover a large colour gamut, but still, they couldn’t match the consistency in colour depth and vibrancy of OLEDs.
Contrary to the LCDs, OLEDs offer the best colour performance as they do not depend upon the backlighting. Moreover, it covers a larger colour gamut that offers a wide colour spectrum to the viewers and the colour saturation, depth, and gradient are also better than the LEDs.
- Brightness and contrast
Although LCDs can achieve a higher level of brightness that makes them a good fit for a lighted environment, their brightness depends upon the capability of the backlight. Furthermore, the contrast ratio is also lower compared to the OLEDs because the backlight is always on.
OLEDs can achieve very high levels of brightness which makes them ideal for dark and bright environments both. OLEDs are renowned for offering the best contrast ratio as the pixels are not dependent on the backlight. Their ability to emit the light on their own enables them to achieve true blacks that enhance the overall depth and richness of the display.
- Resolution and detail
Both LCDs and OLEDs come in a variety of resolution options ranging from Ultra HD to 4K Ultra HD resolution. The higher the resolution of the display, the higher the detailing will be. However, OLEDs offer better detail and image sharpness. LCDs struggle in detailing due to the backlight bleeding from neighbouring pixels.
- Response time and refresh rate
The speed at which a pixel can change from one colour to another is referred to as response time and the refresh rate means how many times per second the display updates the image. The higher response time and refresh rate results in smoother motion and reduced motion blur.
OLEDs have higher response time and refresh rate because of the faster pixels’ response time, which allows them to turn on and off the pixels quickly.

4. Practical Concerns
- Energy efficiency
As the LCDs use a constant backlight source for illumination, whether the LCD is used in a bright environment or a darker one, the energy consumption remains consistent. But as the pixels in OLEDS self-illuminates, it causes variation in energy consumption.
This can be understood as the bright images and high screen brightness levels consume more power, whereas the display of dark images consumes less as the pixels are turned off completely. This means that the OLEDs are more energy-efficient because of their ability to turn off the pixels.
- Durability of the screen
In terms of longevity, LCDs are more reliable for long-term use as the backlights last for years. The organic material used in OLEDs can degrade over time and you may experience reduced brightness or colour accuracy.
- Viewing experience
If you are looking for a display screen for bright environments, you should buy LCDs because of their high brightness levels. Even in the sunlight, the screen remains unaffected due to backlighting.
OLEDs also go well in bright environments, but they perform best in dark settings. No matter what the position of the viewer is in, OLED offers excellent viewing angles with consistent colours and contrast.
5. Cost Analysis
- Initial cost
The pricing of both LCD and OLED goes up and down with the advancements in model, size, brand, and resolution. But if you compare the LCD with OLED, LCD is a cheaper option which is a perfect choice for people who are short on budget.
As the OLEDs offer advanced technology and excellent viewing experience, their prices are higher than the prices of LCDs. Their price range varies from $1,200 to $2,000 or more depending upon their size and resolution.
- Long-term costs
LCD displays generally boast a longer lifespan compared to their OLED counterparts. Their robust construction makes them less susceptible to physical damage and internal issues like burn-in. This translates to fewer repairs and replacements over time, potentially saving you money in the long run.
With proper care, an LCD can last many years without the display quality being affected. However, the super performance of the OLEDs may cause frequent burn-ins and reduction in brightness with time. These issues need to be addressed to keep the display in place. This means that if you are buying an OLED, you must have a maintenance budget as well.
- Value for money
For users who can compromise a bit on the display quality but are looking for a reliable and budget-friendly option, LCDs can offer a good value for money. But for someone who is aiming for a top-notch viewing experience with advanced features and is also willing to pay a higher cost, they should opt for OLEDs.

6. LCD vs OLED: Brief Comparison
To have a better picture of the points of contrast between LCD and OLED, look at this table of comparison.
S.no. | Features | LCD | OLED |
1 | Technology | Uses liquid crystals with LED backlighting | Uses organic compounds that emit light individually |
2 | Backlight | Required | Not required |
3 | Colour performance | Good colour accuracy; varies by panel type | Superior colour accuracy, wider colour gamut |
4 | Cost | More affordable | Costly |
5 | Durability and longevity | More durable compared to OLED | Less durable compared to LCD |
6 | Viewing angles | Limited | Excellent |
7 | Flexibility | Rigid panels; not flexible or bendable | Can be flexible or foldable |
8 | Refresh rate | Lower refresh rates as compared to OLEDs | Excellent refresh rate |
9 | Response time | Generally slower than OLEDs | Faster response time |
10 | Resolution and detail | Good detail retention; resolution varies according to model | Excellent detail retention; resolution varies according to model |
7. LEDSINO: The Perfect Display Solution
Whether it’s buying an LCD or an OLED, it’s crucial to shop for it from a reliable seller to avoid any kind of inconvenience later. The poor quality of the LCD or OLED not only affects the viewing experience but also requires frequent maintenance.
This is why we also came up with a reliable screen seller who offers a wide variety of screens. Whether you are looking for fixed LED displays, stadium LED displays or flexible LED displays, LEDSINO is the perfect spot to find them all that too in top-notch quality.

- Standard Modules Front/Rear Service
- Standard Size: 480×320/960*960mm
- Ultralight Aluminum Profile Cabinet
- Display Can Operate at -20°C to 60°C
- With 3 Years Warranty and 5% Spare Parts
- Optional Hidden Wire – Easy Maintenance
- Rear Screws Securely Fix the LED Modules
- Optional Cabinet Size and Handle Color
- Optional Curved Lock and Angled Cabinet
- With 3 Years Warranty and 5% Spare Parts
8. Summing Up!
LCD and OLED both have their distinct pros and cons. Choosing which one is right for you, an LCD or an OLED, completely depends upon what you are looking for and what is your budget. So, the first thing you need to do before making the purchase is to assess your needs and then find the reliable seller to mitigate the risks of all kinds.



